WHAT IS TESTICULAR CANCER?
Testicular cancer occurs in the testicles (testes), which are located inside the scrotum, a loose bag of skin underneath the penis. The testicles produce male sex hormones and sperm for reproduction.
Compared with other types of cancer, testicular cancer is rare. But testicular cancer is still the most common cancer in American males between the ages of 15 and 35.
Testicular cancer is highly treatable, even when cancer has spread beyond the testicle. Depending on the type and stage of testicular cancer, you may receive one of several treatments, or a combination.
Testicular cancer care at Men’s Health Alaska.
TESTICULAR CANCER SYMPTOMS AND SIGNS INCLUDE:
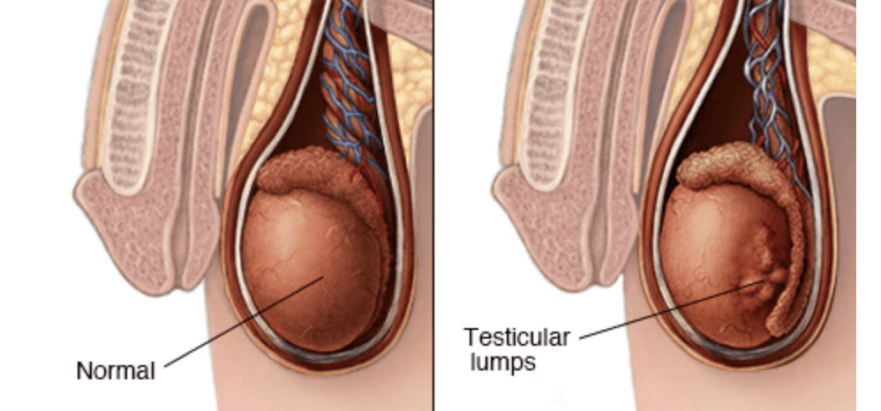
- A lump or enlargement in either testicle
- A feeling of heaviness in the scrotum
- A dull ache in the abdomen or groin
- A sudden collection of fluid in the scrotum
- Pain or discomfort in a testicle or the scrotum
- Enlargement or tenderness of the breasts
- Back pain
- Cancer usually affects only one testicle.
WHEN TO SEE A DOCTOR
See your doctor if you detect any pain, swelling or lumps in your testicles or groin area, especially if these signs and symptoms last longer than two weeks. When you come in to your appointment at Men’s Health Alaska, Dr. Nimeh will screen you for testicular cancer with a physical exam and may also do a testicular ultrasound if necessary.
Click Here to Request an Appointment at Men’s Health Alaska for Testicular Cancer Screening.
CAUSES OF TESTICULAR CANCER
In most cases, the cause of testicular cancer is unknown. Testicular cancer develops when healthy cells in the testes get mutated, according to doctors. Healthy cells divide and expand in a regular pattern to keep your body running smoothly. However, some cells develop defects that cause this growth to spiral out of control – cancer cells continue to divide even when new cells aren’t required. In the testicle, the collecting cells form a mass.
Almost all testicular cancers start in the germ cells of the testicles, which create immature sperm. It’s unclear what causes germ cells to become abnormal and cancerous.
RISK FACTORS
Factors that may increase your risk of testicular cancer include:
- An undescended testicle (cryptorchidism).
- Abnormal testicle development. Conditions that cause testicles to develop abnormally, such as Klinefelter syndrome, may increase your risk of testicular cancer.
- Family history. If family members have had testicular cancer, you may have an increased risk.
- Age. Testicular cancer affects teens and younger men, particularly those between ages 15 and 35. However, it can occur at any age.
- Race. Testicular cancer is more common in white men than in black men.
PREVENTION
There’s no way to prevent testicular cancer.
Some doctors recommend regular testicle self-examinations to identify testicular cancer at its earliest stage, but not all doctors agree.